11613. Best time to buy and sell stock 2
You are given an array of prices, where pricesi contains the price of a stock on the
i-th day.
Each day, you can decide whether to buy
and/or sell stocks. At any given time, you can own at most one stock.
Find the maximum profit that can be
obtained.
Input. The first line contains the size n (n ≤ 105)
of the price array. The second
line contains the price array – n integers, each not exceeding 104.
Output. Print the maximum profit that can be obtained. If it
is impossible to obtain a profit, print 0.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
8 6 3 6 4 2 4 8 3 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
4 5 5 3 2 |
0 |
SOLUTION
greedy
Algorithm analysis
Let’s consider how the stock price changes
every day. If the price increases from day i – 1 to day i, then
we include the difference pricesi – pricesi
– 1 in the total profit.
Example
Consider the first example.
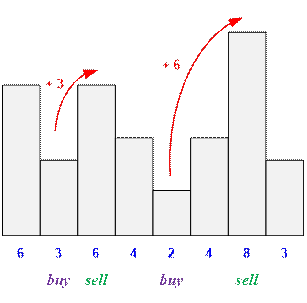
The profit will be 3 + 6 = 9.
Algorithm realization
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
prices.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &prices[i]);
In the variable res, we compute the
maximum possible profit.
res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++)
If the stock price increases from day i
– 1 to day i, then we add the profit prices[i] – prices[i –
1] to the result res.
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1])
res += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
Print
the answer.
printf("%d\n", res);
Python realization
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
prices = list(map(int, input().split()))
In the variable res, we compute the
maximum possible profit.
res = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
If the stock price increases from day i
– 1 to day i, then we add the profit prices[i] – prices[i –
1] to the result res.
if prices[i] > prices[i -
1]:
res += prices[i] - prices[i - 1]
Print
the answer.
print(res)